ReactDOMServer 的作用#
The ReactDOMServer object enables you to render components to static markup.
ReactDOMServer 可以将 react 组件转换为静态的 html
所以,本文主要是为了弄明白 ReactDOMServer 如何将 react 转换为 html
react-dom 将 react 组件转换为 html 的函数有两个: renderToString() 和 renderToStaticMarkup()
主要区别是 renderToStaticMarkup() 不会创建 React 内部使用的额外 DOM 属性,如 data-reactroot。如果你只想把 React 作为简单的静态页面生成器使用,那么使用 renderToStaticMarkup() 是更好的选择,它会比 renderToString() 节省一些字节占用。
import React from "react";
const Header = () => (
<header key="key" className="header">
Header
</header>
);
const Content = ({ name }: { name: string }) => (
<section className="content">Content:{name}</section>
);
const Footer = () => <footer className="footer">Footer</footer>;
const SvgInline = () => (
<svg-inline src="https://yrobot.top/icons/svg-inline.svg"></svg-inline>
);
const Page = () => (
<div className="page">
<Header />
<Content name="yrobot" />
<SvgInline />
<Footer />
</div>
);
export default Page;=> ReactDOMServer.renderToString(<Page />) =>
'<div class="page"><header class="header">Header</header><section class="content">Content:<!-- -->yrobot</section><svg-inline src="https://yrobot.top/icons/svg-inline.svg"></svg-inline><footer class="footer">Footer</footer></div>';疏理 react-dom 源码#
下述源码经过精简,仅保留主流程的逻辑
主干逻辑解析#
function renderToString(
children: ReactNodeList,
options?: ServerOptions
): string {
return renderToStringImpl(children, options);
}function renderToStringImpl(
children: ReactNodeList,
options: void | ServerOptions
): string {
let result = "";
const destination = {
push(chunk) {
if (chunk !== null) {
result += chunk;
}
return true;
},
};
const request = createRequest(children);
startWork(request);
startFlowing(request, destination);
return result;
}这部分代码主要是 renderToString 的主干逻辑,可以看到:
renderToString只是对于renderToStringImpl做了一层封装renderToStringImpl返回result字符串,而result是通过startFlowing(request, destination)利用destination.push来拼接 stream。
通过 log 验证一下#
在 destination.push 中添加一个 log,然后跑一下逻辑:
const destination = {
push(chunk) {
if (chunk !== null) {
result += chunk;
console.log(result);
}
return true;
},
};log 结果: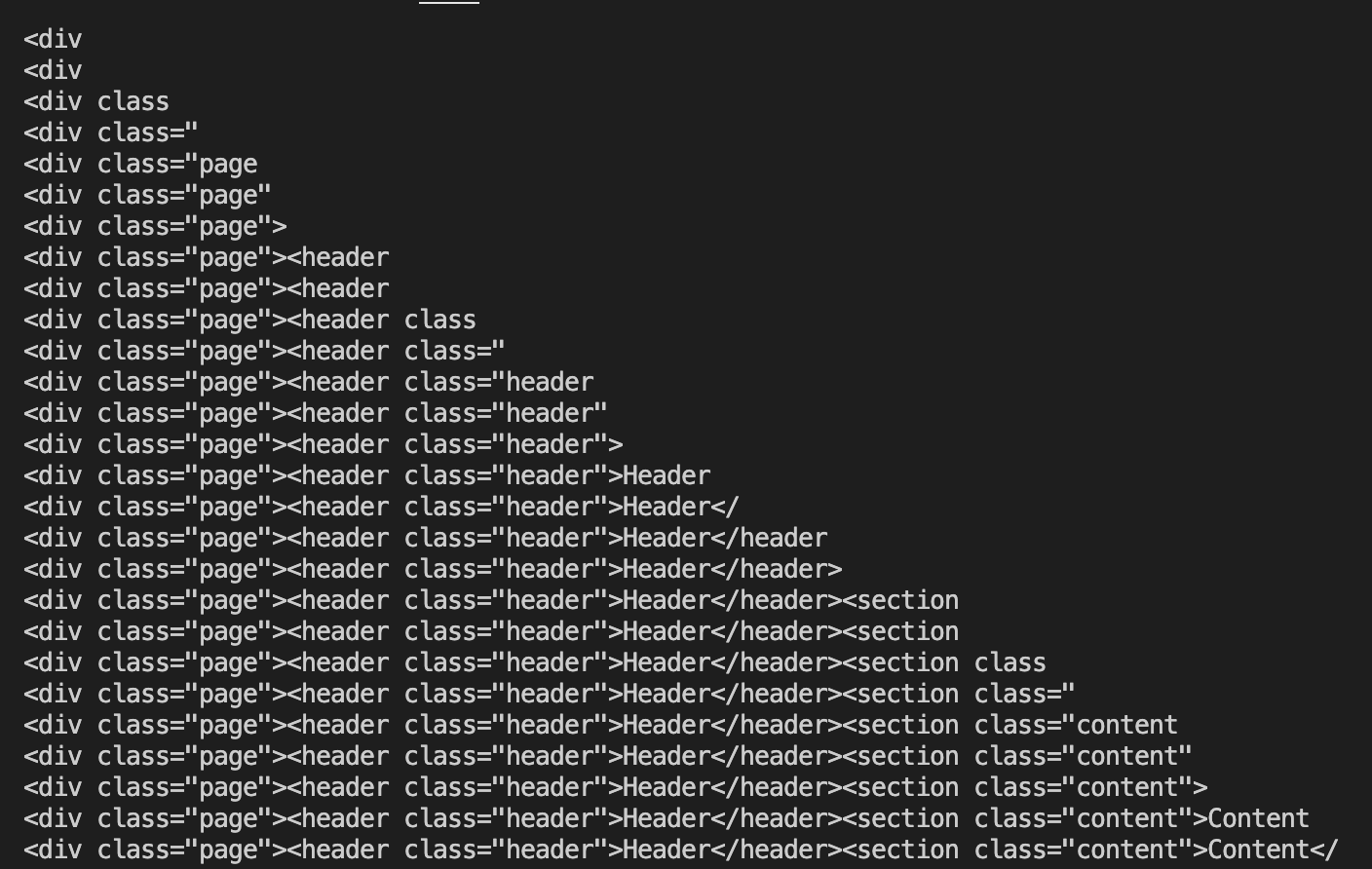
定位主要逻辑位置和数据结构#
在 renderToStringImpl 的 3 个主要步骤之后 log 一下结果
const request = createRequest(children);
console.log("createRequest", request);
startWork(request);
console.log("startWork", request);
startFlowing(request, destination);
console.log("startFlowing", request, destination);log 结果:
createRequest {
destination: null,
responseState: {
bootstrapChunks: [],
startInlineScript: '<script>',
placeholderPrefix: 'P:',
segmentPrefix: 'S:',
boundaryPrefix: 'B:',
idPrefix: '',
nextSuspenseID: 0,
sentCompleteSegmentFunction: false,
sentCompleteBoundaryFunction: false,
sentClientRenderFunction: false,
generateStaticMarkup: true
},
progressiveChunkSize: Infinity,
status: 0,
fatalError: null,
nextSegmentId: 0,
allPendingTasks: 1,
pendingRootTasks: 1,
completedRootSegment: null,
abortableTasks: <ref *1> Set(1) {
{
node: [Object],
ping: [Function: ping],
blockedBoundary: null,
blockedSegment: [Object],
abortSet: [Circular *1],
legacyContext: {},
context: null,
treeContext: [Object],
componentStack: null
}
},
pingedTasks: [
{
node: [Object],
ping: [Function: ping],
blockedBoundary: null,
blockedSegment: [Object],
abortSet: [Set],
legacyContext: {},
context: null,
treeContext: [Object],
componentStack: null
}
],
clientRenderedBoundaries: [],
completedBoundaries: [],
partialBoundaries: [],
}
startWork {
destination: null,
responseState: {
bootstrapChunks: [],
startInlineScript: '<script>',
placeholderPrefix: 'P:',
segmentPrefix: 'S:',
boundaryPrefix: 'B:',
idPrefix: '',
nextSuspenseID: 0,
sentCompleteSegmentFunction: false,
sentCompleteBoundaryFunction: false,
sentClientRenderFunction: false,
generateStaticMarkup: true
},
progressiveChunkSize: Infinity,
status: 0,
fatalError: null,
nextSegmentId: 0,
allPendingTasks: 0,
pendingRootTasks: 0,
completedRootSegment: {
status: 1,
id: -1,
index: 0,
parentFlushed: true,
chunks: [
'<div', ' ', 'class', '="', 'page',
'"', '>', '<header', ' ', 'class',
'="', 'header', '"', '>', 'Header',
'</', 'header', '>', '<section', ' ',
'class', '="', 'content', '"', '>',
'<div', ' ', 'class', '="', 'title',
'"', '>', 'Title', '</', 'div',
'>', '<div', ' ', 'class', '="',
'detail', '"', '>', 'Detail', '</',
'div', '>', '</', 'section', '>',
'<footer', ' ', 'class', '="', 'footer',
'"', '>', 'Footer', '</', 'footer',
'>', '</', 'div', '>'
],
children: [],
formatContext: { insertionMode: 1, selectedValue: null },
boundary: null,
lastPushedText: false,
textEmbedded: false
},
abortableTasks: Set(0) {},
pingedTasks: [],
clientRenderedBoundaries: [],
completedBoundaries: [],
partialBoundaries: [],
}
startFlowing {
destination: { push: [Function: push], destroy: [Function: destroy] },
responseState: {
bootstrapChunks: [],
startInlineScript: '<script>',
placeholderPrefix: 'P:',
segmentPrefix: 'S:',
boundaryPrefix: 'B:',
idPrefix: '',
nextSuspenseID: 0,
sentCompleteSegmentFunction: false,
sentCompleteBoundaryFunction: false,
sentClientRenderFunction: false,
generateStaticMarkup: true
},
progressiveChunkSize: Infinity,
status: 0,
fatalError: null,
nextSegmentId: 0,
allPendingTasks: 0,
pendingRootTasks: 0,
completedRootSegment: null,
abortableTasks: Set(0) {},
pingedTasks: [],
clientRenderedBoundaries: [],
completedBoundaries: [],
partialBoundaries: [],
} { push: [Function: push], destroy: [Function: destroy] }通过 log 可以得出一下 2 点:
- parse 后的主要数据利用 array 的形式储存于 request.completedRootSegment.chunks
- 主要的 parse 工作在 startWork 中完成
由于整个 react-dom/server 还要处理很多场景,如懒加载等,这些场景属于特殊流程分支,逻辑和主要流程类似,本文就不做解析。
后面我们就把注意力主要放在 startWork 是怎么将 react components 解析到 chunks 的。
startWork#
export function startWork(request: Request): void {
setImmediate(() => performWork(request));
}export function performWork(request: Request): void {
const pingedTasks = request.pingedTasks;
let i;
for (i = 0; i < pingedTasks.length; i++) {
const task = pingedTasks[i];
retryTask(request, task);
}
}function retryTask(request: Request, task: Task): void {
const segment = task.blockedSegment;
if (segment.status !== PENDING) return;
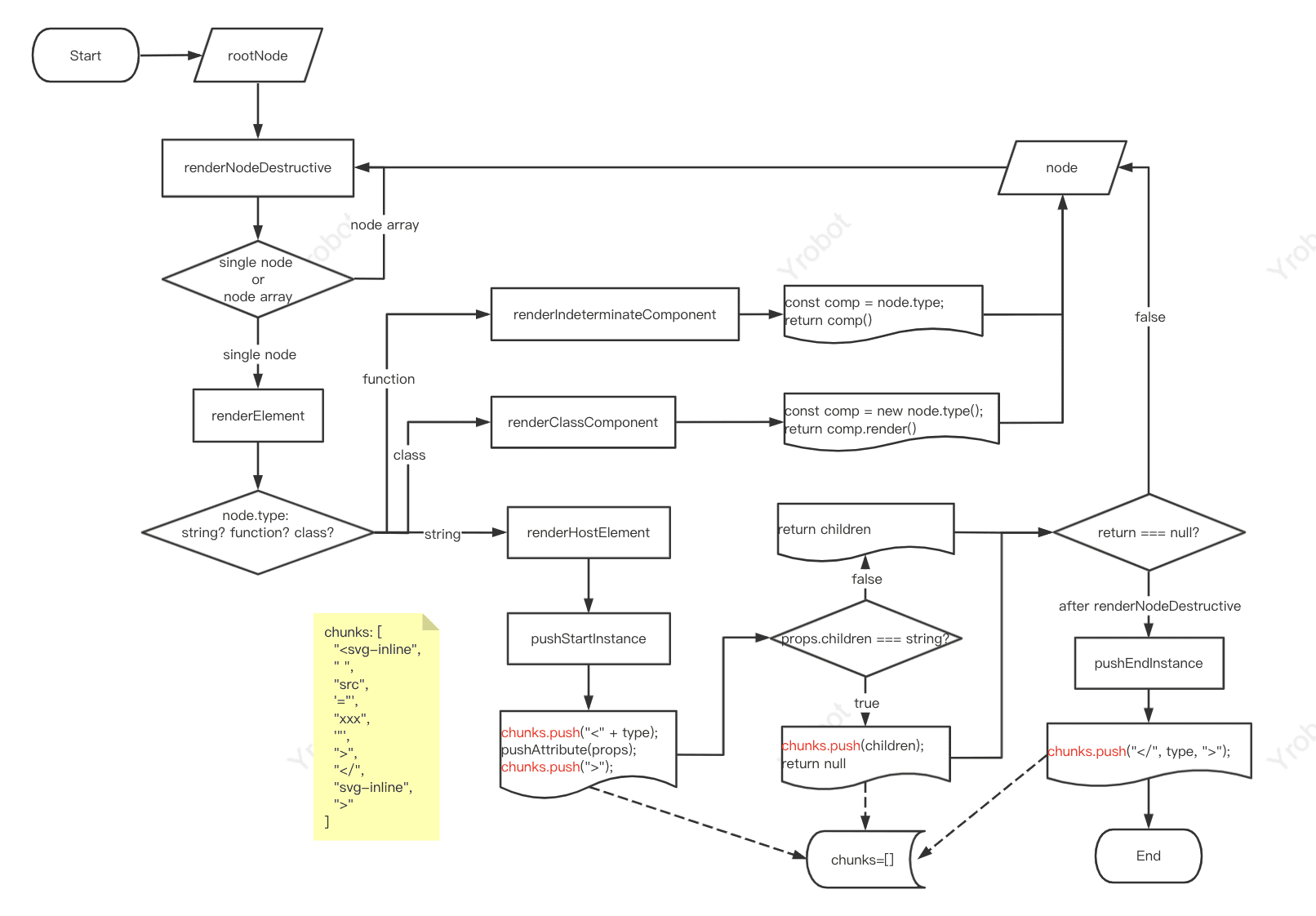
renderNodeDestructive(request, task, task.node); // nodes => chunks
task.abortSet.delete(task);
segment.status = COMPLETED;
finishedTask(request, task.blockedBoundary, segment);
}chunks = task.blockedSegment.chunks = segment.chunks
function renderNodeDestructive(
request: Request,
task: Task,
node: ReactNodeList
): void {
task.node = node;
if (isArray(node)) {
for (let i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
renderNodeDestructive(request, task, children[i]);
}
return;
}
if (typeof node === "object" && node !== null) {
switch ((node: any).$$typeof) {
case REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE: {
const element: React$Element<any> = (node: any);
const type = element.type;
const props = element.props;
const ref = element.ref;
renderElement(request, task, type, props, ref);
return;
}
}
}
}可以看到 renderNodeDestructive 是一个递归函数,它从 rootNode 开始递归,利用 renderElement 对每一个节点进行处理。
我们后面就着重解析 renderElement 是怎么将 node 转化为 html string 的
在解读 renderElement 之前,我们需要先了解 node 的结构#
推荐优先阅读《React 是怎么运行起来的》
node 的结构如下:
{
'$$typeof': Symbol(react.element), // symbol
type: [Function: Page], // string|function|object
key: null,
ref: null,
props: {},
_owner: null,
_store: {}
}简单的解释一下:
$$typeof: 表示 node 的类型,这里的类型是 Symbol(react.element),表示一个 ReactElementtype: 表示 tag name, 可能的类型包括 string、function。- html tag 在这里就是 string,比如'div';
- react hooks component 在这里就是 function, 比如 [Function: Page]
key: 节点的 key 属性ref: 节点的 ref 属性props: 节点的剩余属性的集合
<type key ref {...props} />renderElement#
function renderElement(
request: Request,
task: Task,
type: any,
props: Object,
ref: any
): void {
if (typeof type === "function") {
if (type.prototype && type.prototype.isReactComponent) {
renderClassComponent(request, task, type, props);
return;
} else {
renderIndeterminateComponent(request, task, type, props);
return;
}
}
if (typeof type === "string") {
renderHostElement(request, task, type, props);
return;
}
// ...other types handlers
throw new Error(
"Element type is invalid: expected a string (for built-in " +
"components) or a class/function (for composite components) " +
`but got: ${type == null ? type : typeof type}.${info}`
);
}Hooks Component Handler#
function renderIndeterminateComponent(
request: Request,
task: Task,
Component: any,
props: any
): void {
const value = renderWithHooks(request, task, Component, props, {});
renderNodeDestructive(request, task, value);
}renderWithHooks 将会调用 Component ,并且返回一个 ReactNode。
将这个 ReactNode 重新利用 renderNodeDestructive 进行递归,直到 type 变为 string 类型,即 html tag 本身。
html tag handler#
function renderHostElement(
request: Request,
task: Task,
type: string,
props: Object
): void {
const segment = task.blockedSegment;
// 处理 开始标签 和 节点props
/* ...[
"<svg-inline",
" ",
"src",
'="',
"https://yrobot.top/icons/svg-inline.svg",
'"',
">",
]*/
const children = pushStartInstance(
segment.chunks,
type,
props,
request.responseState,
segment.formatContext
);
// 递归处理 children 节点
renderNodeDestructive(request, task, children);
// 处理 结束标签
// ...['</', 'svg-inline', '>']
pushEndInstance(segment.chunks, type, props);
}export function pushStartInstance(
target: Array<Chunk | PrecomputedChunk>,
type: string,
props: Object,
responseState: ResponseState,
formatContext: FormatContext
): ReactNodeList {
switch (type) {
// Special tags
case "select":
return pushStartSelect(target, props, responseState);
case "option":
return pushStartOption(target, props, responseState, formatContext);
case "textarea":
return pushStartTextArea(target, props, responseState);
case "input":
return pushInput(target, props, responseState);
case "menuitem":
return pushStartMenuItem(target, props, responseState);
case "title":
return pushStartTitle(target, props, responseState);
// Newline eating tags
case "listing":
case "pre": {
return pushStartPreformattedElement(target, props, type, responseState);
}
// Omitted close tags
case "area":
case "base":
case "br":
case "col":
case "embed":
case "hr":
case "img":
case "keygen":
case "link":
case "meta":
case "param":
case "source":
case "track":
case "wbr": {
return pushSelfClosing(target, props, type, responseState);
}
case "annotation-xml":
case "color-profile":
case "font-face":
case "font-face-src":
case "font-face-uri":
case "font-face-format":
case "font-face-name":
case "missing-glyph": {
return pushStartGenericElement(target, props, type, responseState);
}
case "html": {
if (formatContext.insertionMode === ROOT_HTML_MODE) {
target.push(DOCTYPE);
}
return pushStartGenericElement(target, props, type, responseState);
}
default: {
if (type.indexOf("-") === -1 && typeof props.is !== "string") {
// Generic element
return pushStartGenericElement(target, props, type, responseState);
} else {
// Custom element
return pushStartCustomElement(target, props, type, responseState);
}
}
}
}export function pushEndInstance(
target: Array<Chunk | PrecomputedChunk>,
type: string,
props: Object
): void {
switch (type) {
case "area":
case "base":
case "br":
case "col":
case "embed":
case "hr":
case "img":
case "input":
case "keygen":
case "link":
case "meta":
case "param":
case "source":
case "track":
case "wbr": {
break;
}
default: {
target.push("</", type, ">");
}
}
}function pushStartGenericElement(
target: Array<Chunk | PrecomputedChunk>,
props: Object,
tag: string,
responseState: ResponseState
): ReactNodeList {
target.push("<" + tag); // ...['<div']
let children = null;
let innerHTML = null;
for (const propKey in props) {
if (hasOwnProperty.call(props, propKey)) {
const propValue = props[propKey];
if (propValue == null) {
continue;
}
switch (propKey) {
case "children":
children = propValue;
break;
case "dangerouslySetInnerHTML":
innerHTML = propValue;
break;
default:
// 处理 react props
// ...[' ', 'class', '="', 'page', '"',]
pushAttribute(target, responseState, propKey, propValue);
break;
}
}
}
target.push(">"); // ...['>']
pushInnerHTML(target, innerHTML, children);
if (typeof children === "string") {
target.push(encodeHTMLTextNode(children));
return null;
}
return children;
}function pushAttribute(
target: Array<Chunk | PrecomputedChunk>,
responseState: ResponseState,
name: string,
value: string | boolean | number | Function | Object // not null or undefined
): void {
// 将 react element prop 转换为 html tag prop
// 具体逻辑参看 https://github.com/facebook/react/blob/HEAD/packages/react-dom/src/server/ReactDOMServerFormatConfig.js#L418
// 本文不展开赘述
}主要逻辑的流程图#